Driver:MIPS: Difference between revisions
Pmackinlay (talk | contribs) |
Pmackinlay (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
* The "mh" package is damaged and cannot be installed successfully from the currently available installation media. | * The "mh" package is damaged and cannot be installed successfully from the currently available installation media. | ||
* It is recommended to skip the disk space check, as it can be quite time-consuming and is unnecessary if using a sufficiently-sized disk. | * It is recommended to skip the disk space check, as it can be quite time-consuming and is unnecessary if using a sufficiently-sized disk. | ||
* It is recommended to skip the | * It is recommended to skip the network configuration steps, as they may cause <code>inst</code> to abort if unable to copy rsh configuration files from the host. | ||
A minimal installation (root, rc2030, usr) should take about 10 minutes, after which the system should be shut down with <code>telinit</code>. | A minimal installation (root, rc2030, usr) should take about 10 minutes, after which the system should be shut down with <code>telinit</code>. | ||
| Line 161: | Line 161: | ||
mips_miniroot.png|RISC/os Miniroot|alt=A screenshot of RISC/os booted from the miniroot | mips_miniroot.png|RISC/os Miniroot|alt=A screenshot of RISC/os booted from the miniroot | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Booting RISC/os == | == Booting RISC/os == | ||
Once installation is complete, the MIPS monitor may be configured to boot RISC/os normally: | Once installation is complete, the MIPS monitor may be configured to boot RISC/os normally: | ||
Revision as of 09:33, 10 June 2019
MIPS
This article and the corresponding MAME driver focus on computers sold by MIPS Computer Systems which use MIPS R2000/R3000 processors and run RISC/os (also known as UMIPS), a port of UNIX System V release 3 with BSD extensions.
Introduction
Status
Hardware
| Model | Board | CPU | Clock | Slots | Disk | Package | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/500 | R2300 | R2000 | 5MHz | VME | ESDI | ||
| M/800 | R2600 | R2000 | 8MHz | VME | ESDI | ||
| M/1000 | R2800 | R2000 | 10MHz | VME | ESDI | ||
| M/120-3 | R2400 | R2000 | 12.5MHz | PC-AT | SCSI | Deskside | aka Intrepid |
| M/120-5 | R2400 | R2000 | 16MHz | PC-AT | SCSI | Deskside | |
| M/180 | R2400 | ||||||
| M/2000-6 | R3200 | R3000 | 20MHz | VMEx13 | SMD | Rack Cabinet | |
| M/2000-8 | R3200 | R3000 | 25MHz | VMEx13 | SMD | Rack Cabinet | |
| M/2000-? | RB3125 | R3000 | 33MHz | ||||
| RC2030 | I2000 | R2000 | 16MHz | SCSI | Desktop | aka M/12, Jupiter | |
| RS2030 | I2000 | R2000 | 16MHz | SCSI | Desktop | aka M/12, Jupiter | |
| RC3230 | R3030 | R3000 | 25MHz | PC-ATx1 | SCSI | Desktop | aka M/20, Pizazz |
| RS3230 | R3030 | R3000 | 25MHz | PC-ATx1 | SCSI | Desktop | aka M/20, Pizazz, Magnum 3000 |
| RC3240 | R3000 | 25MHz | PC-ATx4 | SCSI | Deskside | M/120 with CPU-board upgrade | |
| RC3330 | R3000 | 33MHz | PC-AT | SCSI | Desktop | ||
| RS3330 | R3000 | 33MHz | PC-AT | SCSI | Desktop | ||
| RC3260 | R3000 | 25MHz | VMEx7 | SCSI | Pedestal | ||
| RC3360 | RB3133 | R3000 | 33MHz | VME | SCSI | Pedestal | |
| RC3370 | RB3133 | ||||||
| RC6260 | R6300 | R6000 | 66MHz | VME | SCSI | Pedestal | |
| RC6280 | R6300 | R6000 | 66MHz | VMEx6 | SMD | Data Center | |
| RC6380-100 | R6000x1 | 66MHz | VME | SMD | Data Center | ||
| RC6380-200 | R6000x2 | 66MHz | VME | SMD | Data Center | ||
| RC6380-400 | R6000x4 | 66MHz | VME | SMD | Data Center |
Preparation
Prerequisites
TODO: mame version, riscos files, tap adapter
Network
TODO: set up the bfs and rsh networking tools and environment.
Storage
Use chdman createhd to prepare a new CHD for the operating system installation, and then chdman addmeta to apply a manufacturer string used to identify the drive make/model information that will be returned by the SCSI INQUIRY command.
chdman createhd -o riscos.chd -c none -chs 1731,15,80 chdman addmeta -i riscos.chd -t IDNT -vt "SEAGATE ST11200N 1.00"
The SCSI INQUIRY response data (defined by the IDNT meta-data tag in the CHD) should consist of an 8 character manufacturer name, 16 character model number, and 4 character version number, all left justified and padded with spaces.
Configuration
TODO: mame configuration
mame64 rs2030 -hard riscos.chd
Installing RISC/os
Environment
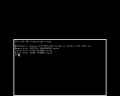
After powering on the system, you should be presented with the MIPS Monitor prompt. The help command shows the syntax recognized, and additional information may be found in the manual[2].
To complete a network installation, it's necessary to set the system TCP/IP address to one compatible with the external networking environment, using the setenv command. The current environment settings are retained in non-volatile memory, and may be displayed using printenv.
setenv netaddr 192.168.137.2
Format
The format utility allows disks to be formatted, partitioned and labelled. There are two versions of this utility, with format.std being used for all but the RC2030 and RS2030 systems, which have their own dedicated version format.2030.
Launch the applicable format utility using the boot command, being sure to provide the path name matching your BFS or TFTP data path.
boot -f bfs()tree/stand/format.2030
Once format is launched, accept the defaults for all prompts except the following, adjusting the disk geometry to match that provided to chdman.
| Prompt | Response |
|---|---|
| name of device | dksd |
| device parameters | 13 |
| number of cylinders | 1731 |
| number heads in vol 0 | 15 |
| number sectors per track | 80 |
| number bytes per sector | 512 |
| media defect command | q |
| write new volume header | y |
The utility will exit to the monitor once the volume header has been written.
Miniroot Installation
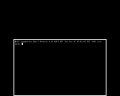
As with the format utility, there are two versions of the standalone shell (sash). sash.std is used for all but the RC2030 and RS2030 systems which have their own dedicated version, sash.2030. Launch sash as follows.
boot -f bfs()tree/stand/sash.2030
From the sash prompt, use the cp command to copy the miniroot filesystem from TFTP to the boot partition of the hard disk.
cp bfs()root.fs dksd(0,0,1)
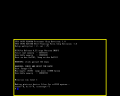
This process should take around 10 minutes to complete.
RISC/os Installation
After the miniroot has been copied to disk, RISC/os may be booted using it as a root file system with a kernel loaded from TFTP.
boot -f bfs()unix.i2000_std root=sdc0d0s1
From the miniroot shell prompt, configure the environment to specify a network installation and the name of the installation server, and start the RISC/os installation utility inst.
From=en Server=host inst
Most of the prompts from inst are fairly self-explanatory, however there are some which may require further guidance:
- The "remote package root" and "remote packaging information tree" responses must correspond to the "tree" and "umips4.52" directories within the RISC/os network installation structure respectively.
- The "mh" package is damaged and cannot be installed successfully from the currently available installation media.
- It is recommended to skip the disk space check, as it can be quite time-consuming and is unnecessary if using a sufficiently-sized disk.
- It is recommended to skip the network configuration steps, as they may cause
instto abort if unable to copy rsh configuration files from the host.
A minimal installation (root, rc2030, usr) should take about 10 minutes, after which the system should be shut down with telinit.
telinit 0
-
MIPS Monitor
-
MIPS Standalone Shell
-
RISC/os Miniroot
Booting RISC/os
Once installation is complete, the MIPS monitor may be configured to boot RISC/os normally:
setenv bootfile dksd(,,8)sash
After this, the command auto may be used to boot RISC/os, or the monitor configured to boot automatically at system start:
setenv bootmode c
References
The following are various documents pertaining to MIPS computer systems.
| Reference | Title | Date | Links |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Title | MmmYY | [3] |